جامعة بنها - كمية العموم قسم الرياضيات المستوي الرابع )علوم حاسب( يوم االمتحان: االحد تاريخ االمتحان: 1024 / 21 / 12 المادة :
|
|
|
- Shanon Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 جامعة بنها - كمية العموم قسم الرياضيات المستوي الرابع )علوم حاسب( يوم االمتحان: االحد تاريخ االمتحان: 1024 / 21 / 12 م المادة : بنية الحاسب )124 رس( الممتحن: د/ مصعب عبد الحميد محمد حسان مدرس بقسم الرياضيات بكمية العموم االسئمة و اإلجابة نموذج كاممة ورقة
2 Answer the following question Question 1. (12 marks) A- Define microoperations, instruction code, common bus system, assembler? (4 marks) B- Consider 128K X 16 memory. How many address lines does it have? How many data lines it have? What is its total capacity in Kbytes? What will be the total capacity if the address lines are changed to 20 lines without changing the word size? (3 marks) C- Draw the bus system for two registers such that each register has eight bits? (5 marks) Question 2. (14 marks) A- List the registers in the basic computer and write a description of their function and the number of bits that they contain? (4 marks) B- Write the instruction cycle steps in details? (6 marks) C- What is the difference between a direct and indirect address instruction? How many references to memory are needed for each type of instruction to bring an operand into a processor register? (4 marks) Question 3. (12 marks) A- For each timing signal, show the contents in hexadecimal of registers PC, AR, DR, IR, and SC of the basic computer when an ISZ indirect instruction is fetched from memory and executed. The initial content of PC is 7FE. The content of memory at address 7FE is EA9F. The content of memory at address A9F is 0C35. The content of memory at address C35 is FFFF. (4 marks) -Page 1-
3 B- List the memory reference instructions and for each instruction write operation decoder and symbolic description? (5 marks) C- List the rules of the assembly language? (3 marks) Question 4. (10 marks) A- List the categories of programs written for a computer? (3 marks) B- Write assembly language program to calculate the expression a+b-c? (4 marks) C- Given the common bus system of the basic computer, the following register transfers are to be executed in the system? For each transfer, specify: (1) the binary value that must be applied to bus select inputs S 2, S 1, and S 0 ; (2) the register whose LD control input must be active (if any); (3) a memory read or write operation (if needed) (3 marks) (i) AR PC (ii) IR M[AR] (iii) M[AR] TR Best Wishes Dr. Mosab Abd El-Hameed -Page 2-
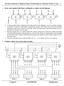
4 Answer of Question 1 A- microoperations are operations executed on data stored in one or more registers instruction code is a group of bits that instructs the computer to perform a specific operation (sequence of microoperations). It is divided into parts (basic part is the operation part) common bus system is a scheme for transferring information between registers in a multiple-register configuration The translation of symbolic program into binary is done by a special program called an assembler B- This memory has -17 address lines data lines. - Total capacity of (128 x 1024 x 16) / (1024 x 8) = 256 Kbytes - If the address lines are changed to 20 lines without changing the word size, the memory will be 1024K X 16. Then the total capacity will be (1024 x 1024 x 16) / (1024 x 8) = 2048 Kbytes C- Register B Register A B 7 B 6 B 5 B 4 B 3 B 2 B 1 B 0 A 7 A 6 A 5 A 4 A 3 A 2 A 1 A 0 B 7 A 7 B 6 A 6 B 5 A 5 B 4 A 4 B 3 A 3 B 2 A 2 B 1 A 1 B 0 A 0 Mux7 Mux6 Mux5 Mux4 Mux3 Mux2 Mux1 Mux0 S 1 S 0 S 1 S 0 S 1 S 0 S 1 S 0 S 1 S 0 S 1 S 0 S 1 S 0 S 1 S 0 8-Line Common Bus
5 Answer of Question 2 A- List of BC registers: DR 16 Data Register Holds memory operand AR 12 Address Register Holds address for memory AC 16 Accumulator Processor register IR 16 Instruction Register Holds instruction code PC 12 Program Counter Holds address of instruction TR 16 Temporary Register Holds temporary data INPR 8 Input Register Holds input character OUTR 8 Output Register Holds output character B- Instruction Cycle Steps: 1- Fetch an instruction from memory 2- Decode the instruction 3- Read the effective address from memory if the instruction has an indirect address 4- Execute the instruction This cycle repeats indefinitely unless a HALT instruction is encountered Instruction Cycle Fetch and Decode 1- Initially, the Program Counter (PC) is loaded with the address of the first instruction in the program 2- The sequence counter SC is cleared to 0, providing a decoded timing signal T 0 3- After each clock pulse, SC is incremented by one, so that the timing signals go through a sequence T 0, T 1, T 2, and so on T 0 : AR PC (this is essential) The address of the instruction is moved to AR. T 1 : IR M[AR], PC PC+1 The instruction is fetched from the memory to IR, and the PC is incremented. T 2 : D 0,, D 7 Decode IR(12-14), AR IR(0-11), I IR(15) Next figure shows the instruction cycle flowchart. we can determine the type of instruction (see in the figure). For example: D'7IT3: AR M[AR] D'7I'T3: Nothing D7I'T3: Execute a register-reference instr. D7IT3: Execute an input-output instr.
6 C- Direct Address Instruction has its operand address specified directly in the instruction, but the Indirect Address Instruction has the address of the operand s address, i.e. not directly the address of the operand. Direct Address Instruction: needs 2 visits to memory. The 1 st one is to fetch the instruction, 2 nd is to bring the operand.
7 Indirect Address Instruction: needs 3 visits to memory. The 1 st one is to fetch the instruction, 2 nd is to bring the operand address. And the 3 rd is to bring the operand itself. Answer of Question 3 A- Given 7FE X X X 0 T0 7FE 7FE X X 1 T1 7FF 7FE X EA9F 2 T2 7FF A9F X EA9F 3 T3 7FF C35 X EA9F 4 T4 7FF C35 FFFF EA9F 5 T5 7FF C EA9F 6 T6 800 C EA9F 0 B- Symbol Operation Symbolic Description AND D 0 AC AC M[AR] ADD D 1 AC AC + M[AR], E C out LDA D 2 AC M[AR] STA D 3 M[AR] AC BUN D 4 PC AR BSA D 5 M[AR] PC, PC AR + 1 ISZ D 6 M[AR] M[AR] + 1, if M[AR] + 1 = 0 then PC PC+1 C- Each line of an assembly language program is arranged in three columns called fields: 1-The Label field: May be empty or specify a symbolic address. 2- The Instruction field: Specifies a machine instruction or pseudo instruction. 3- The Comment field: May be ORG Lab Lab, ADD op1 / this is an add operation. Label Instruction Comment Answer of Question 4 A- The categories of programs written for a computer: 1- Binary code. This is a sequence of instructions and operands in binary that list the exact representation of instructions as they appear in computer memory.
8 2- Octal or hexadecimal code. This is an equivalent translation of the binary code or hexadecimal. 3- Symbolic code. The user employs symbols (letters, numerals, or special characters) for the operation part, the address part, and other parts of the instruction code. Each symbolic instruction can be translated into one binary coded instruction. 4- High-level programming languages. These are special languages developed to reflect the procedures used in the solution of a problem rather than be concerned with the computer hardware behavior. For example, C++, Java, C#. B- Suppose we calculate ORG 0 /Origin of program is location 0 LDA A /Load operand from location A ADD B /Add operand from location B STA D /Store sum in location D LDA C /Load operand from location C CMA /Complement AC INC /Increment AC ADD D /Add operand from location D STA E /Store the result in location E HLT /Halt computer A, DEC 83 /Decimal operand B, DEC 23 /Decimal operand C, DEC 15 /Decimal operand D, DEC 0 /Sum stored in location D E, DEC 0 /The result stored in location E END /End of symbolic program C-
Chapter 5. Computer Architecture Organization and Design. Computer System Architecture Database Lab, SANGJI University
 Chapter 5. Computer Architecture Organization and Design Computer System Architecture Database Lab, SANGJI University Computer Architecture Organization and Design Instruction Codes Computer Registers
Chapter 5. Computer Architecture Organization and Design Computer System Architecture Database Lab, SANGJI University Computer Architecture Organization and Design Instruction Codes Computer Registers
Unit II Basic Computer Organization
 1. Define the term. Internal Organization-The internal organization of a digital system is defined by the sequence of microoperations it performs on data stored in its registers. Program- A program is
1. Define the term. Internal Organization-The internal organization of a digital system is defined by the sequence of microoperations it performs on data stored in its registers. Program- A program is
Computer architecture Assignment 3
 Computer architecture Assignment 3 1- An instruction at address 14E in the basic computer has I=0, an operation code of the AND instruction, and an address part equal to 109(all numbers are in hexadecimal).
Computer architecture Assignment 3 1- An instruction at address 14E in the basic computer has I=0, an operation code of the AND instruction, and an address part equal to 109(all numbers are in hexadecimal).
CHAPTER SIX BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN
 CHAPTER SIX BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN 6.1. Instruction Codes The organization of a digital computer defined by: 1. The set of registers it contains and their function. 2. The set of instructions
CHAPTER SIX BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN 6.1. Instruction Codes The organization of a digital computer defined by: 1. The set of registers it contains and their function. 2. The set of instructions
csitnepal Unit 3 Basic Computer Organization and Design
 Unit 3 Basic Computer Organization and Design Introduction We introduce here a basic computer whose operation can be specified by the resister transfer statements. Internal organization of the computer
Unit 3 Basic Computer Organization and Design Introduction We introduce here a basic computer whose operation can be specified by the resister transfer statements. Internal organization of the computer
UNIT:2 BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN
 1 UNIT:2 BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN 2.1 Instruction Codes 2.2 Computer Registers AC or Accumulator, Data Register or DR, the AR or Address Register, program
1 UNIT:2 BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN 2.1 Instruction Codes 2.2 Computer Registers AC or Accumulator, Data Register or DR, the AR or Address Register, program
Computer Organization (Autonomous)
 Computer Organization (Autonomous) UNIT II Sections - A & D Prepared by Anil Kumar Prathipati, Asst. Prof., Dept. of CSE. SYLLABUS Basic Computer Organization and Design: Instruction codes Stored Program
Computer Organization (Autonomous) UNIT II Sections - A & D Prepared by Anil Kumar Prathipati, Asst. Prof., Dept. of CSE. SYLLABUS Basic Computer Organization and Design: Instruction codes Stored Program
CHAPTER 5 Basic Organization and Design Outline Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle
 CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 5 Basic Organization and Design Outline Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions
CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 5 Basic Organization and Design Outline Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions
5-1 Instruction Codes
 Chapter 5: Lo ai Tawalbeh Basic Computer Organization and Design 5-1 Instruction Codes The Internal organization of a digital system is defined by the sequence of microoperations it performs on data stored
Chapter 5: Lo ai Tawalbeh Basic Computer Organization and Design 5-1 Instruction Codes The Internal organization of a digital system is defined by the sequence of microoperations it performs on data stored
BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN
 1 BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions Input-Output and Interrupt Complete
1 BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions Input-Output and Interrupt Complete
Basic Computer Organization and Design Part 2/3
 Basic Computer Organization and Design Part 2/3 Adapted by Dr. Adel Ammar Computer Organization Basic Computer Instructions Basic Computer Instruction Format Memory-Reference Instructions (OP-code = 000
Basic Computer Organization and Design Part 2/3 Adapted by Dr. Adel Ammar Computer Organization Basic Computer Instructions Basic Computer Instruction Format Memory-Reference Instructions (OP-code = 000
BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN
 1 BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions Input-Output and Interrupt Complete
1 BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions Input-Output and Interrupt Complete
C.P.U Organization. Memory Unit. Central Processing Unit (C.P.U) Input-Output Processor (IOP) Figure (1) Digital Computer Block Diagram
 C.P.U Organization 1.1 Introduction A computer system is sometimes subdivided into two functional entities "Hardware" and "Software". The H/W of the computer consists of all the electronic components and
C.P.U Organization 1.1 Introduction A computer system is sometimes subdivided into two functional entities "Hardware" and "Software". The H/W of the computer consists of all the electronic components and
Computer Architecture and Organization: L06: Instruction Cycle
 Computer Architecture and Organization: L06: Instruction Cycle By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com 1 Outlines 1. Fetch and decode 2. Determine the Type of Instruction
Computer Architecture and Organization: L06: Instruction Cycle By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com 1 Outlines 1. Fetch and decode 2. Determine the Type of Instruction
Faculty of Engineering Systems & Biomedical Dept. First Year Cairo University Sheet 6 Computer I
 aculty of Engineering Systems & Biomedical Dept. irst Year Cairo University Sheet 6 Computer I 1. Choose rue or alse for each of the following statements a) In a direct addressing mode instruction, the
aculty of Engineering Systems & Biomedical Dept. irst Year Cairo University Sheet 6 Computer I 1. Choose rue or alse for each of the following statements a) In a direct addressing mode instruction, the
BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN
 BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions Input-Output and Interrupt Complete
BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions Input-Output and Interrupt Complete
Basic Computer Organization - Designing your first computer. Acknowledgment: Most of the slides are adapted from Prof. Hyunsoo Yoon s slides.
 Basic Computer Organization - Designing your first computer Acknowledgment: Most of the slides are adapted from Prof. Hyunsoo Yoon s slides. 1 This week- BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Instruction
Basic Computer Organization - Designing your first computer Acknowledgment: Most of the slides are adapted from Prof. Hyunsoo Yoon s slides. 1 This week- BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Instruction
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION INDEX UNIT-II PPT SLIDES Srl. No. Module as per Session planner Lecture No. PPT Slide No. 1. Register Transfer language 2. Register Transfer Bus and memory transfers 3. Arithmetic
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION INDEX UNIT-II PPT SLIDES Srl. No. Module as per Session planner Lecture No. PPT Slide No. 1. Register Transfer language 2. Register Transfer Bus and memory transfers 3. Arithmetic
Midterm Examination # 2 Wednesday, March 18, Duration of examination: 75 minutes
 Page 1 of 8 School of Computer Science 60-265-01 Computer Architecture and Digital Design Winter 2009 Midterm Examination # 2 Wednesday, March 18, 2009 Student Name: First Name Family Name Student ID Number:
Page 1 of 8 School of Computer Science 60-265-01 Computer Architecture and Digital Design Winter 2009 Midterm Examination # 2 Wednesday, March 18, 2009 Student Name: First Name Family Name Student ID Number:
Computer Organization and Design
 CSE211 Computer Organization and Design Lecture : 3 Tutorial: 1 Practical: 0 Credit: 4 KIDS Labs 1 Unit 1 : Basics of Digital Electronics Introduction Logic Gates Flip Flops Decoder Encoder Multiplexers
CSE211 Computer Organization and Design Lecture : 3 Tutorial: 1 Practical: 0 Credit: 4 KIDS Labs 1 Unit 1 : Basics of Digital Electronics Introduction Logic Gates Flip Flops Decoder Encoder Multiplexers
Programming Level A.R. Hurson Department of Computer Science Missouri University of Science & Technology Rolla, Missouri
 Programming Level A.R. Hurson Department of Computer Science Missouri University of Science & Technology Rolla, Missouri 65409 hurson@mst.edu A.R. Hurson 1 Programming Level Computer: A computer with a
Programming Level A.R. Hurson Department of Computer Science Missouri University of Science & Technology Rolla, Missouri 65409 hurson@mst.edu A.R. Hurson 1 Programming Level Computer: A computer with a
Introduction. Machine Language. Assembly Language. Assembler. Program Loops. Programming Arithmetic and Logic Operations.
 Computer System AA rc hh ii tec ture( 66 )) PROGRAMMING THE BASIC COMPUTER Introduction Machine Language Assembly Language Assembler Program Loops Programming Arithmetic and Logic Operations Subroutines
Computer System AA rc hh ii tec ture( 66 )) PROGRAMMING THE BASIC COMPUTER Introduction Machine Language Assembly Language Assembler Program Loops Programming Arithmetic and Logic Operations Subroutines
PSIM: Processor SIMulator (version 4.2)
 PSIM: Processor SIMulator (version 4.2) by Charles E. Stroud, Professor Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Auburn University July 23, 2003 ABSTRACT A simulator for a basic stored program computer
PSIM: Processor SIMulator (version 4.2) by Charles E. Stroud, Professor Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Auburn University July 23, 2003 ABSTRACT A simulator for a basic stored program computer
CHAPTER SEVEN PROGRAMMING THE BASIC COMPUTER
 CHAPTER SEVEN 71 Introduction PROGRAMMING THE BASIC COMPUTER A computer system as it was mentioned before in chapter 1, it is subdivided into two functional parts: 1 Hardware, which consists of all physical
CHAPTER SEVEN 71 Introduction PROGRAMMING THE BASIC COMPUTER A computer system as it was mentioned before in chapter 1, it is subdivided into two functional parts: 1 Hardware, which consists of all physical
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Lecture 1: Digital logic circuits The digital computer is a digital system that performs various computational tasks. Digital computers use the binary number system, which has two
Computer Architecture Lecture 1: Digital logic circuits The digital computer is a digital system that performs various computational tasks. Digital computers use the binary number system, which has two
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND DIGITAL DESIGN
 SPECIAL MAKEUP - FINAL EXAMINATION COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND DIGITAL DESIGN 03-60-265-01 S C H O O L O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E - U N I V E R S I T Y O F W I N D S O R Fall 2008 Last Name: First
SPECIAL MAKEUP - FINAL EXAMINATION COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND DIGITAL DESIGN 03-60-265-01 S C H O O L O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E - U N I V E R S I T Y O F W I N D S O R Fall 2008 Last Name: First
Blog -
 . Instruction Codes Every different processor type has its own design (different registers, buses, microoperations, machine instructions, etc) Modern processor is a very complex device It contains Many
. Instruction Codes Every different processor type has its own design (different registers, buses, microoperations, machine instructions, etc) Modern processor is a very complex device It contains Many
Computer Architecture
 http://www.bsccsit.com/ Computer Architecture CSC. 201 Third Semester Prepared By: Arjun Singh Saud Special thanks to Mr. Arjun Singh Saud for providing this valuable note! Chapter 1 Data representation
http://www.bsccsit.com/ Computer Architecture CSC. 201 Third Semester Prepared By: Arjun Singh Saud Special thanks to Mr. Arjun Singh Saud for providing this valuable note! Chapter 1 Data representation
SCRAM Introduction. Philipp Koehn. 19 February 2018
 SCRAM Introduction Philipp Koehn 19 February 2018 This eek 1 Fully work through a computer circuit assembly code Simple but Complete Random Access Machine (SCRAM) every instruction is 8 bit 4 bit for op-code:
SCRAM Introduction Philipp Koehn 19 February 2018 This eek 1 Fully work through a computer circuit assembly code Simple but Complete Random Access Machine (SCRAM) every instruction is 8 bit 4 bit for op-code:
session 7. Datapath Design
 General Objective: Determine the hardware requirement of a digital computer based on its instruction set. Specific Objectives: Describe the general concepts in designing the data path of a digital computer
General Objective: Determine the hardware requirement of a digital computer based on its instruction set. Specific Objectives: Describe the general concepts in designing the data path of a digital computer
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital
 Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital hardware modules that accomplish a specific information-processing task. Digital systems vary in
Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital hardware modules that accomplish a specific information-processing task. Digital systems vary in
Class Notes. Dr.C.N.Zhang. Department of Computer Science. University of Regina. Regina, SK, Canada, S4S 0A2
 Class Notes CS400 Part VI Dr.C.N.Zhang Department of Computer Science University of Regina Regina, SK, Canada, S4S 0A2 C. N. Zhang, CS400 83 VI. CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT 1 Set 1.1 Addressing Modes and Formats
Class Notes CS400 Part VI Dr.C.N.Zhang Department of Computer Science University of Regina Regina, SK, Canada, S4S 0A2 C. N. Zhang, CS400 83 VI. CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT 1 Set 1.1 Addressing Modes and Formats
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1
 Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1 1. Draw and explain 4 bit binary arithmetic or adder circuit diagram. A binary parallel adder is digital function that produces
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1 1. Draw and explain 4 bit binary arithmetic or adder circuit diagram. A binary parallel adder is digital function that produces
Chapter 16. Control Unit Operation. Yonsei University
 Chapter 16 Control Unit Operation Contents Micro-Operation Control of the Processor Hardwired Implementation 16-2 Micro-Operations Micro-Operations Micro refers to the fact that each step is very simple
Chapter 16 Control Unit Operation Contents Micro-Operation Control of the Processor Hardwired Implementation 16-2 Micro-Operations Micro-Operations Micro refers to the fact that each step is very simple
COMARCH. COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE TERM 3 SY COMPUTER ENGINEERING DE LA SALLE UNIVERSITY Quiz 1
 COMARCH. COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE TERM 3 SY 2015 2016 COMPUTER ENGINEERING DE LA SALLE UNIVERSITY Quiz 1 1. Draw the logic symbol of the component whose operations are specified by the following microoperations:
COMARCH. COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE TERM 3 SY 2015 2016 COMPUTER ENGINEERING DE LA SALLE UNIVERSITY Quiz 1 1. Draw the logic symbol of the component whose operations are specified by the following microoperations:
Roll No TCS 402/TIT 402
 Roll No TCS 402/TIT 402 Mid Term Examination March 2016 B.Tech (IV Semester) Computer Organization Time: Two (2) Hrs. Maximum Marks: 60 NOTE: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) This question paper contains three questions
Roll No TCS 402/TIT 402 Mid Term Examination March 2016 B.Tech (IV Semester) Computer Organization Time: Two (2) Hrs. Maximum Marks: 60 NOTE: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) This question paper contains three questions
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE
 REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences. Lab 4: Introduction to MARIE
 Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences CS 3401 Assembly Language 4 Lab 4: Introduction to MARIE Objectives: The main objective of this lab is to get you familiarized with MARIE a simple computer
Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences CS 3401 Assembly Language 4 Lab 4: Introduction to MARIE Objectives: The main objective of this lab is to get you familiarized with MARIE a simple computer
UNIT - V MEMORY P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, VBIT
 UNIT - V MEMORY P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents Memory: Introduction, Random-Access memory, Memory decoding, ROM, Programmable Logic Array, Programmable Array Logic, Sequential programmable
UNIT - V MEMORY P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents Memory: Introduction, Random-Access memory, Memory decoding, ROM, Programmable Logic Array, Programmable Array Logic, Sequential programmable
Effective Approach for Teaching Computer System Architecture
 Effective Approach for Teaching Computer System Architecture K. M. Hasam 1, Akhlaq A Khan 2, M. Saleem 3, M Riaz Moghal 3, asir Mahmood 4, M. Adnan 5, Tanveer Akhtar 6 1,3 Department of Electrical Engineering,
Effective Approach for Teaching Computer System Architecture K. M. Hasam 1, Akhlaq A Khan 2, M. Saleem 3, M Riaz Moghal 3, asir Mahmood 4, M. Adnan 5, Tanveer Akhtar 6 1,3 Department of Electrical Engineering,
Assembly Language Programming of 8085
 Assembly Language Programming of 8085 Topics 1. Introduction 2. Programming model of 8085 3. Instruction set of 8085 4. Example Programs 5. Addressing modes of 8085 6. Instruction & Data Formats of 8085
Assembly Language Programming of 8085 Topics 1. Introduction 2. Programming model of 8085 3. Instruction set of 8085 4. Example Programs 5. Addressing modes of 8085 6. Instruction & Data Formats of 8085
THE MICROPROCESSOR Von Neumann s Architecture Model
 THE ICROPROCESSOR Von Neumann s Architecture odel Input/Output unit Provides instructions and data emory unit Stores both instructions and data Arithmetic and logic unit Processes everything Control unit
THE ICROPROCESSOR Von Neumann s Architecture odel Input/Output unit Provides instructions and data emory unit Stores both instructions and data Arithmetic and logic unit Processes everything Control unit
Chapter 2 Instruction Set Architecture
 Chapter 2 Instruction Set Architecture Course Outcome (CO) - CO2 Describe the architecture and organization of computer systems Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
Chapter 2 Instruction Set Architecture Course Outcome (CO) - CO2 Describe the architecture and organization of computer systems Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL
 MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL Hardwired Control Unit: When the control signals are generated by hardware using conventional logic design techniques, the control unit is said to be hardwired. Micro programmed
MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL Hardwired Control Unit: When the control signals are generated by hardware using conventional logic design techniques, the control unit is said to be hardwired. Micro programmed
M. Sc (CS) (II Semester) Examination, Subject: Computer System Architecture Paper Code: M.Sc-CS-203. Time: Three Hours] [Maximum Marks: 60
![M. Sc (CS) (II Semester) Examination, Subject: Computer System Architecture Paper Code: M.Sc-CS-203. Time: Three Hours] [Maximum Marks: 60 M. Sc (CS) (II Semester) Examination, Subject: Computer System Architecture Paper Code: M.Sc-CS-203. Time: Three Hours] [Maximum Marks: 60](/thumbs/87/96339673.jpg) M. Sc (CS) (II Semester) Examination, 2012-13 Subject: Computer System Architecture Paper Code: M.Sc-CS-203 Time: Three Hours] [Maximum Marks: 60 Note: Question Number 1 is compulsory. Answer any four
M. Sc (CS) (II Semester) Examination, 2012-13 Subject: Computer System Architecture Paper Code: M.Sc-CS-203 Time: Three Hours] [Maximum Marks: 60 Note: Question Number 1 is compulsory. Answer any four
Computer Architecture Programming the Basic Computer
 4. The Execution of the EXCHANGE Instruction The EXCHANGE routine reads the operand from the effective address and places it in DR. The contents of DR and AC are interchanged in the third microinstruction.
4. The Execution of the EXCHANGE Instruction The EXCHANGE routine reads the operand from the effective address and places it in DR. The contents of DR and AC are interchanged in the third microinstruction.
Notes: The Marie Simulator
 The Accumulator (AC) is the register where calculations are performed. To add two numbers together, a) load the first number into the accumulator with a Load instruction b) Add the second number to the
The Accumulator (AC) is the register where calculations are performed. To add two numbers together, a) load the first number into the accumulator with a Load instruction b) Add the second number to the
The Institution of Engineers - Sri Lanka
 / The Institution of Engineers - Sri Lanka PART III- EXAMINATION 2012 311- COMPUTER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Time Allowed: 3 hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This paper contains 8 questions in 5 pages 2.
/ The Institution of Engineers - Sri Lanka PART III- EXAMINATION 2012 311- COMPUTER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Time Allowed: 3 hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This paper contains 8 questions in 5 pages 2.
CC312: Computer Organization
 CC312: Computer Organization Dr. Ahmed Abou EL-Farag Dr. Marwa El-Shenawy 1 Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer
CC312: Computer Organization Dr. Ahmed Abou EL-Farag Dr. Marwa El-Shenawy 1 Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer
The MARIE Architecture
 The MARIE Machine Architecture that is Really Intuitive and Easy. We now define the ISA (Instruction Set Architecture) of the MARIE. This forms the functional specifications for the CPU. Basic specifications
The MARIE Machine Architecture that is Really Intuitive and Easy. We now define the ISA (Instruction Set Architecture) of the MARIE. This forms the functional specifications for the CPU. Basic specifications
CPU Design John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 1
 CPU Design 1997 John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 1 Outline Register organization ALU design Stacks Instruction formats and types Addressing modes 1997 John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 2 We
CPU Design 1997 John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 1 Outline Register organization ALU design Stacks Instruction formats and types Addressing modes 1997 John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 2 We
Blog - https://anilkumarprathipati.wordpress.com/
 Control Memory 1. Introduction The function of the control unit in a digital computer is to initiate sequences of microoperations. When the control signals are generated by hardware using conventional
Control Memory 1. Introduction The function of the control unit in a digital computer is to initiate sequences of microoperations. When the control signals are generated by hardware using conventional
Computer Organization and Architecture
 Computer Organization and Architecture Dr Binu P Chacko Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Prajyoti Niketan College, Pudukad, THRISSUR Instruction Codes Computer organization is defined
Computer Organization and Architecture Dr Binu P Chacko Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Prajyoti Niketan College, Pudukad, THRISSUR Instruction Codes Computer organization is defined
MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL:-
 MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL:- Two methods of implementing control unit are Hardwired Control & Micro-Programmed Control. Hardwired: - when the control signals are generated by hardware using conventional logic
MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL:- Two methods of implementing control unit are Hardwired Control & Micro-Programmed Control. Hardwired: - when the control signals are generated by hardware using conventional logic
Computer Organization II CMSC 3833 Lecture 33
 Term MARIE Definition Machine Architecture that is Really Intuitive and Easy 4.8.1 The Architecture Figure s Architecture Characteristics: Binary, two s complement Stored program, fixed word length Word
Term MARIE Definition Machine Architecture that is Really Intuitive and Easy 4.8.1 The Architecture Figure s Architecture Characteristics: Binary, two s complement Stored program, fixed word length Word
Problem Set 1 Solutions
 CSE 260 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design Jon Turner Problem Set 1 Solutions 1. Give a brief definition of each of the following parts of a computer system: CPU, main memory, floating
CSE 260 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design Jon Turner Problem Set 1 Solutions 1. Give a brief definition of each of the following parts of a computer system: CPU, main memory, floating
Register Transfer and Micro-operations
 Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus Memory Transfer Micro-operations Some Application of Logic Micro Operations Register Transfer and Micro-operations Learning Objectives After reading this
Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus Memory Transfer Micro-operations Some Application of Logic Micro Operations Register Transfer and Micro-operations Learning Objectives After reading this
Copyright 2000 N. AYDIN. All rights reserved. 1
 Computer Architecture Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr http://www.yildiz.edu.tr/~naydin A virtual processor for understanding instruction cycle The Visible Virtual Machine (VVM) 1 2 The
Computer Architecture Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr http://www.yildiz.edu.tr/~naydin A virtual processor for understanding instruction cycle The Visible Virtual Machine (VVM) 1 2 The
Computer Architecture and Organization: L09: CPU Organization
 Computer Architecture and Organization: L09: CPU Organization By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 CAO, by Dr. A.H. Abdul Hafez, CE Dept. HKU
Computer Architecture and Organization: L09: CPU Organization By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 CAO, by Dr. A.H. Abdul Hafez, CE Dept. HKU
Chapter. Computer Architecture
 Chapter 4 Computer Architecture Figure 4.1 Input device Central processing unit Main memory Output device Bus Data flow Control Figure 4.2 Central processing unit () Status bits ( ) Accumulator ( ) Index
Chapter 4 Computer Architecture Figure 4.1 Input device Central processing unit Main memory Output device Bus Data flow Control Figure 4.2 Central processing unit () Status bits ( ) Accumulator ( ) Index
Mark II Aiken Relay Calculator
 Introduction to Embedded Microcomputer Systems Lecture 6.1 Mark II Aiken Relay Calculator 2.12. Tutorial 2. Arithmetic and logical operations format descriptions examples h 8-bit unsigned hexadecimal $00
Introduction to Embedded Microcomputer Systems Lecture 6.1 Mark II Aiken Relay Calculator 2.12. Tutorial 2. Arithmetic and logical operations format descriptions examples h 8-bit unsigned hexadecimal $00
Mini-Computer PDP-8 ISA Simulator Design and Verification
 Mini-Computer PDP-8 ISA Simulator Design and Verification Students Authors: Rajath Mavathur Basavaraj Ranjith Kumar M Supervised By: Dr. Elarabi Why ISA simulator Simulation at the ISA -Instruction Set
Mini-Computer PDP-8 ISA Simulator Design and Verification Students Authors: Rajath Mavathur Basavaraj Ranjith Kumar M Supervised By: Dr. Elarabi Why ISA simulator Simulation at the ISA -Instruction Set
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 16 Control Unit Operations Rev. 3.2 (2009-10) by Enrico Nardelli 16-1 Execution of the Instruction Cycle It has many elementary phases,
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 16 Control Unit Operations Rev. 3.2 (2009-10) by Enrico Nardelli 16-1 Execution of the Instruction Cycle It has many elementary phases,
Chapter 4. MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer. Chapter 4 Objectives. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 CPU Basics
 Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution.
Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution.
Introduction to Programming
 Introduction to Programming Chapter 2 Microcontrollers Objectives Describe the difference between source code and machine code. Define opcode, operand, and address of an operand. Explain the purpose of
Introduction to Programming Chapter 2 Microcontrollers Objectives Describe the difference between source code and machine code. Define opcode, operand, and address of an operand. Explain the purpose of
Assembly Language Programming of 8085
 Assembly Language Programming of 8085 1. Introduction A microprocessor executes instructions given by the user Instructions should be in a language known to the microprocessor Microprocessor understands
Assembly Language Programming of 8085 1. Introduction A microprocessor executes instructions given by the user Instructions should be in a language known to the microprocessor Microprocessor understands
Chapter 3 : Control Unit
 3.1 Control Memory Chapter 3 Control Unit The function of the control unit in a digital computer is to initiate sequences of microoperations. When the control signals are generated by hardware using conventional
3.1 Control Memory Chapter 3 Control Unit The function of the control unit in a digital computer is to initiate sequences of microoperations. When the control signals are generated by hardware using conventional
MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL
 1 MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL Control Memory Sequencing Microinstructions Microprogram Example Design of Control nit Microinstruction Format Nanostorage and Nanoprogram 2 Implementation of Control nit COMPARISON
1 MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL Control Memory Sequencing Microinstructions Microprogram Example Design of Control nit Microinstruction Format Nanostorage and Nanoprogram 2 Implementation of Control nit COMPARISON
UNIT-II. Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
 Page1 UNIT-II Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes Data Transfer And Manipulation Program Control Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Introduction:
Page1 UNIT-II Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes Data Transfer And Manipulation Program Control Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Introduction:
CS 265. Computer Architecture. Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng.
 CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. Part 3: von Neumann Architecture von Neumann Architecture Our goal: understand the basics of von Neumann architecture, including memory, control unit
CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. Part 3: von Neumann Architecture von Neumann Architecture Our goal: understand the basics of von Neumann architecture, including memory, control unit
Chapter 10 Computer Design Basics
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 10 Computer Design Basics Part 2 A Simple Computer Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Terms of Use (Hyperlinks are active in View
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 10 Computer Design Basics Part 2 A Simple Computer Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Terms of Use (Hyperlinks are active in View
INTELLIGENCE PLUS CHARACTER - THAT IS THE GOAL OF TRUE EDUCATION UNIT-I
 UNIT-I 1. List and explain the functional units of a computer with a neat diagram 2. Explain the computer levels of programming languages 3. a) Explain about instruction formats b) Evaluate the arithmetic
UNIT-I 1. List and explain the functional units of a computer with a neat diagram 2. Explain the computer levels of programming languages 3. a) Explain about instruction formats b) Evaluate the arithmetic
UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT
 UNIT-III 1 KNREDDY UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT Register Transfer: Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Micro operations Logic
UNIT-III 1 KNREDDY UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT Register Transfer: Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Micro operations Logic
There are four registers involved in the fetch cycle: MAR, MBR, PC, and IR.
 CS 320 Ch. 20 The Control Unit Instructions are broken down into fetch, indirect, execute, and interrupt cycles. Each of these cycles, in turn, can be broken down into microoperations where a microoperation
CS 320 Ch. 20 The Control Unit Instructions are broken down into fetch, indirect, execute, and interrupt cycles. Each of these cycles, in turn, can be broken down into microoperations where a microoperation
A3 Computer Architecture
 A3 Computer Architecture Engineering Science 3rd year A3 Lectures Prof David Murray david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/3co Michaelmas 2000 1 / 1 2: Introduction to the CPU 3A3 Michaelmas
A3 Computer Architecture Engineering Science 3rd year A3 Lectures Prof David Murray david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/3co Michaelmas 2000 1 / 1 2: Introduction to the CPU 3A3 Michaelmas
Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: Ph:
 Serial : LS2_EE_S_Microprocessors_2688 Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: -452462 CLASS TEST 28-9 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Serial : LS2_EE_S_Microprocessors_2688 Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: -452462 CLASS TEST 28-9 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
CSE100 Lecture03 Machines, Instructions, and Programs Introduction to Computer Systems
 Machines, Instructions, and Introduction to Computer Systems M.A. Computer Science and Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology Dhaka 1000, Bangladesh CSE, BUET, 2009 MARIE Machine
Machines, Instructions, and Introduction to Computer Systems M.A. Computer Science and Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology Dhaka 1000, Bangladesh CSE, BUET, 2009 MARIE Machine
 Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3120 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud http://iweb.tntech.edu/mmahmoud/ mmahmoud@tntech.edu Outline 1.1 Computer hardware organization 1.1.1 Number System 1.1.2 Computer hardware
Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3120 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud http://iweb.tntech.edu/mmahmoud/ mmahmoud@tntech.edu Outline 1.1 Computer hardware organization 1.1.1 Number System 1.1.2 Computer hardware
TYPICAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 TYPICAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS PART-I Each Question carries 2 marks. OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Choose the correct or best alternative in the following: Q.1 In Reverse Polish notation, expression A*B+C*D is
TYPICAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS PART-I Each Question carries 2 marks. OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Choose the correct or best alternative in the following: Q.1 In Reverse Polish notation, expression A*B+C*D is
EE 3170 Microcontroller Applications
 EE 317 Microcontroller Applications Lecture 5 : Instruction Subset & Machine Language: Introduction to the Motorola 68HC11 - Miller 2.1 & 2.2 Based on slides for ECE317 by Profs. Davis, Kieckhafer, Tan,
EE 317 Microcontroller Applications Lecture 5 : Instruction Subset & Machine Language: Introduction to the Motorola 68HC11 - Miller 2.1 & 2.2 Based on slides for ECE317 by Profs. Davis, Kieckhafer, Tan,
Chapter 1. Microprocessor architecture ECE Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud.
 Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3130 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud The slides are copyright protected. It is not permissible to use them without a permission from Dr Mahmoud http://www.cae.tntech.edu/~mmahmoud/
Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3130 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud The slides are copyright protected. It is not permissible to use them without a permission from Dr Mahmoud http://www.cae.tntech.edu/~mmahmoud/
MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL
 1 MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL Control Memory Sequencing Microinstructions Microprogram Example Design of Control nit Microinstruction Format Nanostorage and Nanoprogram External input (IR) Next address generator
1 MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL Control Memory Sequencing Microinstructions Microprogram Example Design of Control nit Microinstruction Format Nanostorage and Nanoprogram External input (IR) Next address generator
STRUCTURE OF DESKTOP COMPUTERS
 Page no: 1 UNIT 1 STRUCTURE OF DESKTOP COMPUTERS The desktop computers are the computers which are usually found on a home or office desk. They consist of processing unit, storage unit, visual display
Page no: 1 UNIT 1 STRUCTURE OF DESKTOP COMPUTERS The desktop computers are the computers which are usually found on a home or office desk. They consist of processing unit, storage unit, visual display
Wednesday, February 4, Chapter 4
 Wednesday, February 4, 2015 Topics for today Introduction to Computer Systems Static overview Operation Cycle Introduction to Pep/8 Features of the system Operational cycle Program trace Categories of
Wednesday, February 4, 2015 Topics for today Introduction to Computer Systems Static overview Operation Cycle Introduction to Pep/8 Features of the system Operational cycle Program trace Categories of
Chapter 4. MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer
 Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution.
Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution.
Arab Open University. Computer Organization and Architecture - T103
 Arab Open University Computer Organization and Architecture - T103 Reference Book: Linda Null, Julia Lobur, The essentials of Computer Organization and Architecture, Jones & Bartlett, Third Edition, 2012.
Arab Open University Computer Organization and Architecture - T103 Reference Book: Linda Null, Julia Lobur, The essentials of Computer Organization and Architecture, Jones & Bartlett, Third Edition, 2012.
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3. Annalisa Massini /2015
 Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - 2014/2015 Von Neumann Architecture 2 Summary of the traditional computer architecture: Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - 2014/2015 Von Neumann Architecture 2 Summary of the traditional computer architecture: Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
TABLE 8-1. Control Signals for Binary Multiplier. Load. MUL0 Q 0 CAQ sr CAQ. Shift_dec. C out. Load LOADQ. CAQ sr CAQ. Shift_dec P P 1.
 T-192 Control Signals for Binary Multiplier TABLE 8-1 Control Signals for Binary Multiplier Block Diagram Module Microoperation Control Signal Name Control Expression Register A: A 0 Initialize IDLE G
T-192 Control Signals for Binary Multiplier TABLE 8-1 Control Signals for Binary Multiplier Block Diagram Module Microoperation Control Signal Name Control Expression Register A: A 0 Initialize IDLE G
CHAPTER 4: Register Transfer Language and Microoperations
 CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 4: Register Transfer Language and Microoperations Outline Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations
CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 4: Register Transfer Language and Microoperations Outline Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations
CHAPTER 8: Central Processing Unit (CPU)
 CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 8: Central Processing Unit (CPU) Outline Introduction General Register Organization Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes 1 Major Components
CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 8: Central Processing Unit (CPU) Outline Introduction General Register Organization Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes 1 Major Components
CS311 Lecture: The Architecture of a Simple Computer
 CS311 Lecture: The Architecture of a Simple Computer Objectives: July 30, 2003 1. To introduce the MARIE architecture developed in Null ch. 4 2. To introduce writing programs in assembly language Materials:
CS311 Lecture: The Architecture of a Simple Computer Objectives: July 30, 2003 1. To introduce the MARIE architecture developed in Null ch. 4 2. To introduce writing programs in assembly language Materials:
Instruction : A command to the microprocessor to perform a given task on specified data. Each instruction has two parts
 Lecture 4 Instruction : A command to the microprocessor to perform a given task on specified data. Each instruction has two parts One part is the task to be performed, called operation code or opcode in
Lecture 4 Instruction : A command to the microprocessor to perform a given task on specified data. Each instruction has two parts One part is the task to be performed, called operation code or opcode in
EE 5340/7340 Motorola 68HC11 Microcontroler Lecture 1. Carlos E. Davila, Electrical Engineering Dept. Southern Methodist University
 EE 5340/7340 Motorola 68HC11 Microcontroler Lecture 1 Carlos E. Davila, Electrical Engineering Dept. Southern Methodist University What is Assembly Language? Assembly language is a programming language
EE 5340/7340 Motorola 68HC11 Microcontroler Lecture 1 Carlos E. Davila, Electrical Engineering Dept. Southern Methodist University What is Assembly Language? Assembly language is a programming language
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE
 Page 1 1. Which register store the address of next instruction to be executed? A) PC B) AC C) SP D) NONE 2. How many bits are required to address the 128 words of memory? A) 7 B) 8 C) 9 D) NONE 3. is the
Page 1 1. Which register store the address of next instruction to be executed? A) PC B) AC C) SP D) NONE 2. How many bits are required to address the 128 words of memory? A) 7 B) 8 C) 9 D) NONE 3. is the
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition. Chapter 11 Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition Chapter 11 Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats Addressing Modes Immediate Direct Indirect Register Register Indirect Displacement
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition Chapter 11 Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats Addressing Modes Immediate Direct Indirect Register Register Indirect Displacement
MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer
 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Outline Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution. Understand a simple
MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Outline Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution. Understand a simple
CS 31: Intro to Systems Digital Logic. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College February 2, 2016
 CS 31: Intro to Systems Digital Logic Kevin Webb Swarthmore College February 2, 2016 Reading Quiz Today Hardware basics Machine memory models Digital signals Logic gates Circuits: Borrow some paper if
CS 31: Intro to Systems Digital Logic Kevin Webb Swarthmore College February 2, 2016 Reading Quiz Today Hardware basics Machine memory models Digital signals Logic gates Circuits: Borrow some paper if
Architecture & Instruction set of 8085 Microprocessor and 8051 Micro Controller
 of 8085 microprocessor 8085 is pronounced as "eighty-eighty-five" microprocessor. It is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Intel in 1977 using NMOS technology. It has the following configuration 8-bit
of 8085 microprocessor 8085 is pronounced as "eighty-eighty-five" microprocessor. It is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Intel in 1977 using NMOS technology. It has the following configuration 8-bit
Teaching London Computing
 Teaching London Computing CAS London CPD Day 2016 Little Man Computer William Marsh School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science Queen Mary University of London Overview and Aims LMC is a computer
Teaching London Computing CAS London CPD Day 2016 Little Man Computer William Marsh School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science Queen Mary University of London Overview and Aims LMC is a computer
MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL
 1 MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL Control Memory Sequencing Microinstructions Microprogram Example Design of Control nit Microinstruction Format Nanostorage and Nanoprogram 2 Implementation of Control nit COMPARISON
1 MICROPROGRAMMED CONTROL Control Memory Sequencing Microinstructions Microprogram Example Design of Control nit Microinstruction Format Nanostorage and Nanoprogram 2 Implementation of Control nit COMPARISON
